

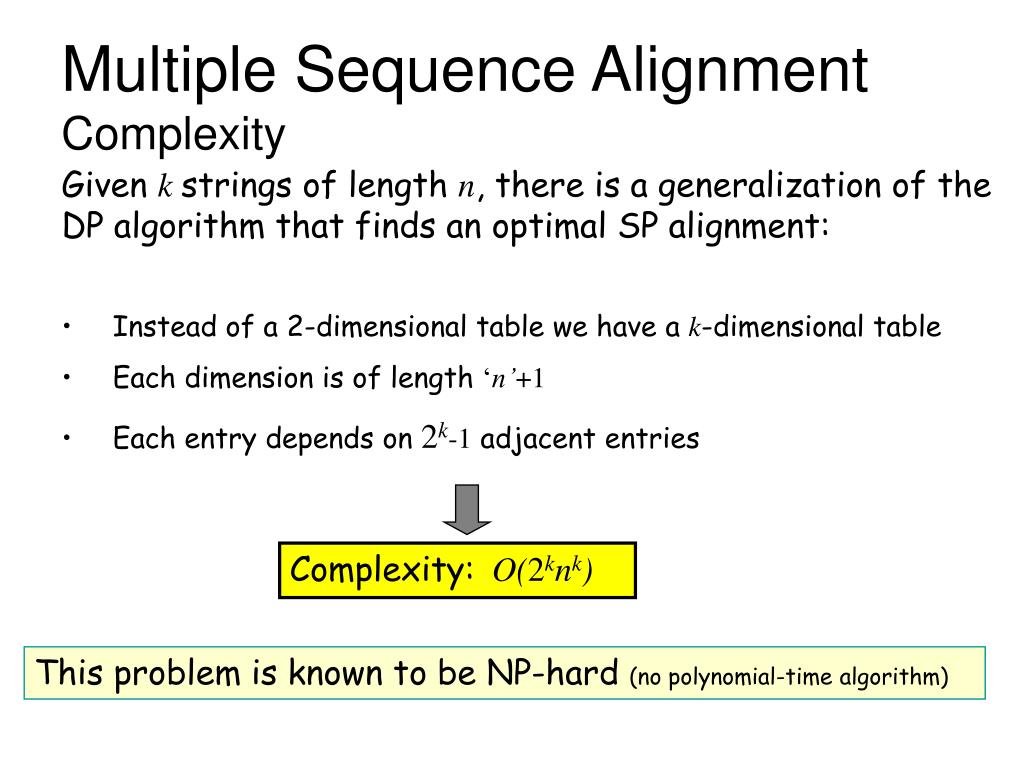
Resulting alignments can be rendered with ESPript. MultAlin is a multiple sequence alignment program with hierarchical clustering.can carry out multiple sequence alignments with ClustalW or MultAlin and resulting outputs can be rendered with ESPript. is an interactive Web server dedicated to protein sequence analysis.T-Coffee is a collection of tools for computing, evaluating and manipulating multiple alignments of DNA, RNA, protein sequences and structures.Arbitrary docking can reveal potential interaction sites on the surface of a protein using docking with a set of 25 random protein "probes". ARDOCK is a Web server for the study of protein surfaces.Several ENDscript representations are produced with ESPript. ENDscript is a friendly Web server, which extracts and renders a comprehensive analysis of primary to quaternary protein structure information in an automated way.Biotool Web servers interfaced with ESPript:.Optional files allow further rendering.The program calculates a similarity score for each residue of the aligned sequences.Its main input is a file of pre-aligned sequences in Clustal, FASTA, MultAlin, or ProDom format.
#Multiple sequence alignment pdf#
#Multiple sequence alignment full size#
This is a direct consequence of its importance in the T cell proliferation pathway.Excerpt from a generated ESPript figure ( full size in PDF) To view the larger and more comprehensive phylogenetic tree, please visist the Phylogenetic Tree section.įrom this multiple sequnece alignment it is concluded that CaMKIV is highly conserved in evolution, mainly its four identified domains. This result will become more relevant when using the tool to make the phylogenetic tree using many more species. This result confirms the validity of the bioinformatics tool in the case of CaMKIV. It is therefore not necessarily representative of the phylogenetic distance between species.ĭespite this, the tree respects the general evolutionary relationship. This small phylogenetic tree was obtained with the COBALT or “ constraint-based alignment tool” on NCBI and is based on protein sequence data. This protein has been predicted using the Swissmodel (an automated protein modelling server), for more information please visit: However, thale cress differs the most, having a longer sequence than the other species, leading to deletions in the alignment. All four domains are exceptionally conserved amongst all the reference species.
Note that the protein is a predicted model, whose sequence stops straight after the Calmodulin-Binding Domain. By the C-terminus of the helix, and of the protein, is the Calmodulin-Binding Domain (blue). At the N-terminus of such helix are the autoinhibitory Domain (magenta) and the PP2A-Binding Domain (cyan), which greatly overlap (depicted as different coloured overlapping dots). The catalytic domain (yellow) makes up almost all of the protein except for the autoinhibitory helix. Shown here all four highly conserved domains of CaMKIV. Scroll over the diagram below and click on the domains to be linked to their explanations. You can gain access to the relevant details of a specific domain by clicking anywhere within the corresponding coloured domain region in the diagram below.
Including species which are phylogenetically very far highlights the parts of the protein which remained conserved throughtout evolution, which is a strong indicator of their importance (shown in image). Finally is thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana), which belongs to a different kingdom. These are followed by chicken ( Gallus gallus), a bird, and by zebrafish ( Danio rerio), a fish, both being genetically more different to mammals. Then follow house mouse ( Mus musculus) and common rat ( Rattus novegicus), both being also mammals. At the top is human ( Homo Sapiens), followed by common chimpanzee ( Pan troglodytes), which is very closely related. Note that the species were arranged in the multiple sequence alignment according to their genetic similarities determined by the phylogenetic tree. Shown below are a multiple sequence alignment of seven different representative CaMKIV across different species their corresponding phylogenetic tree and an image of the protein's conserved domains.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
